India’s aviation journey began with the world’s first airmail flight in 1911 from Allahabad to Naini, evolving into a state monopoly under Indian Airlines in 1953 that stifled competition for decades. This history of over-regulation and inefficiency paved the way for post-1991 liberalization, birthing IndiGo’s dominance but exposing duopoly risks seen in the recent crisis of over 1,600 flight cancellations due to crew shortages and FDTL rules.
Pioneering Flights to Nationalization
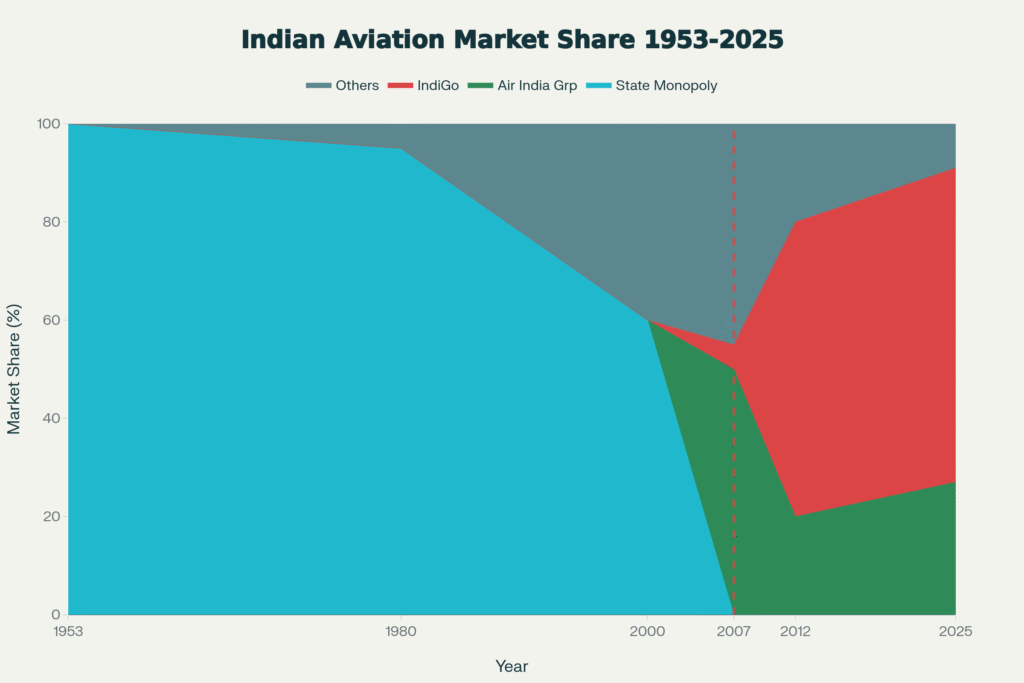
Commercial aviation took off on February 18, 1911, with Henri Pequet’s Humber biplane carrying mail over 6 miles, marking global history. J.R.D. Tata launched Tata Airlines in 1932, rebranded Air India in 1946, but the 1953 Air Corporations Act merged carriers into state giants: Air India for international and Indian Airlines for domestic routes, controlling nearly 100% until the 1990s.
Liberalization and IndiGo’s Rise
Deregulation in 1991 allowed private players, with IndiGo entering in 2006 as a low-cost disruptor amid Indian Airlines’ 2007 merger with Air India, which bloated debts and lost market share. By 2025, IndiGo commands 64% domestic share, Air India Group 27%, forming a duopoly vulnerable to single-point failures like the current crisis.
Duopoly’s Breaking Point: IndiGo Chaos
IndiGo canceled 1,200+ flights in late 2025 from pilot shortages, hiring freezes, and unadjusted FDTL rules despite two years’ notice, crippling airports like Delhi and Mumbai. The monopoly era’s legacy of poor planning echoes here, as dominance bred complacency without crew buffers, forcing government FDTL suspensions.
India’s aviation shifted from rigid control to cutthroat competition, but the IndiGo crisis reveals how historical over-reliance on few players still strands millions.
India’s aviation journey began with the world’s first airmail flight in 1911 from Allahabad to Naini, evolving into a state monopoly under Indian Airlines in 1953 that stifled competition for decades. This history of over-regulation and inefficiency paved the way for post-1991 liberalization, birthing IndiGo’s dominance but exposing duopoly risks seen in the recent crisis of over 1,600 flight cancellations due to crew shortages and FDTL rules.indiatoday+3
References
- https://www.indiatoday.in/business/story/india-aviation-crisis-flight-cancellations-indigo-air-india-flight-https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/indigo-flight-disruption-live-updates-delhi-mumbai-flight-cancelled-news-updates-all-domestic-flights-out-of-delhi-cancelled-till-midnight-today-9755290
- https://www.storyboard18.com/brand-marketing/brand-indigo-in-turbulence-1200-flights-cancelled-shares-slide-govt-probe-sparks-unprecedented-reputational-crisis-85455.htm
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/the-chaos-at-indigo-hit-hard-flight-duty-time-rules-10401830/
- https://www.indmoney.com/blog/stocks/indigo-stock-fall-crisis-explained
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/from-rs-43000-tickets-to-10-hour-delays-how-indigo-disruptions-are-crippling-air-travel-top-developments/articleshow/125763804.cms
- https://www.oag.com/indian-aviation-data
- https://www.apaoindia.com/?page_id=185
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Civil_aviation_in_India
- https://www.granthaalayahpublication.org/Arts-Journal/ShodhKosh/article/download/2745/2467/17198
- https://aviationa2z.com/index.php/2022/08/15/india-at-75-75-key-events-in-civil-aviation-of-india-exclusive/